With the rapid development of bio-mass spectrometry technology, mass spectrometry technology has gradually become the mainstream technology for proteomics analysis. Mass spectrometers have characteristics such as high sensitivity and high resolution, and the quality and reproducibility of sample pretreatment significantly affect the separation and identification capabilities of the mass spectrometer.
Proteomics sample pretreatment processes are complex and time-consuming (traditional proteomics pretreatment requires overnight), and manual operations are prone to errors, causing instability and poor reproducibility in sample pretreatment. There is an urgent need for an automated solution that is easy to operate, efficient, has high safety performance, and strong anti-interference capabilities to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Raykol has launched a new proteomics sample pretreatment workstation, accompanied by the Raykol proteomics sample pretreatment kit, providing a fully automated solution for proteomics sample pretreatment, efficiently achieving automation and standardization of mass spectrometry protein sample pretreatment operations.
The proteomics sample pretreatment solution is suitable for pretreatment work from proteins to peptide mixtures in mass spectrometry detection of samples such as plasma, serum, urine, cells, tissues, etc. The kit utilizes the new solid-phase alkylation reagent SPA materials that covalently react specifically with proteins to achieve high-efficiency protein capture, rapidly remove interfering substances by cleaning the surface of magnetic beads, and perform in-situ solid-phase enzymolysis to obtain proteolytic products. The instrument integrates a refrigeration module, magnetic adsorption module, heating oscillation module, and a gripping hand to achieve automated operations of processes such as protein extraction, reduction, alkylation, and enzymolysis, thereby improving the efficiency and recovery rate of protein sample processing.
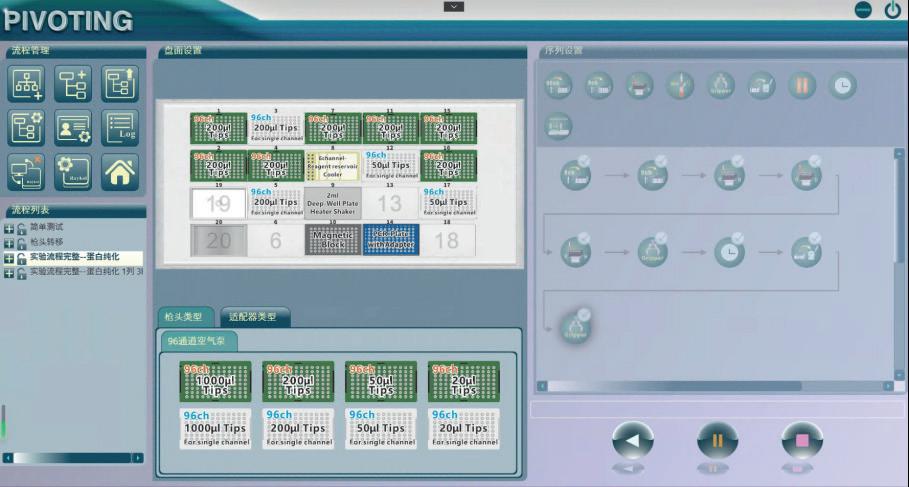
Proteomics Sample Pretreatment Workstation
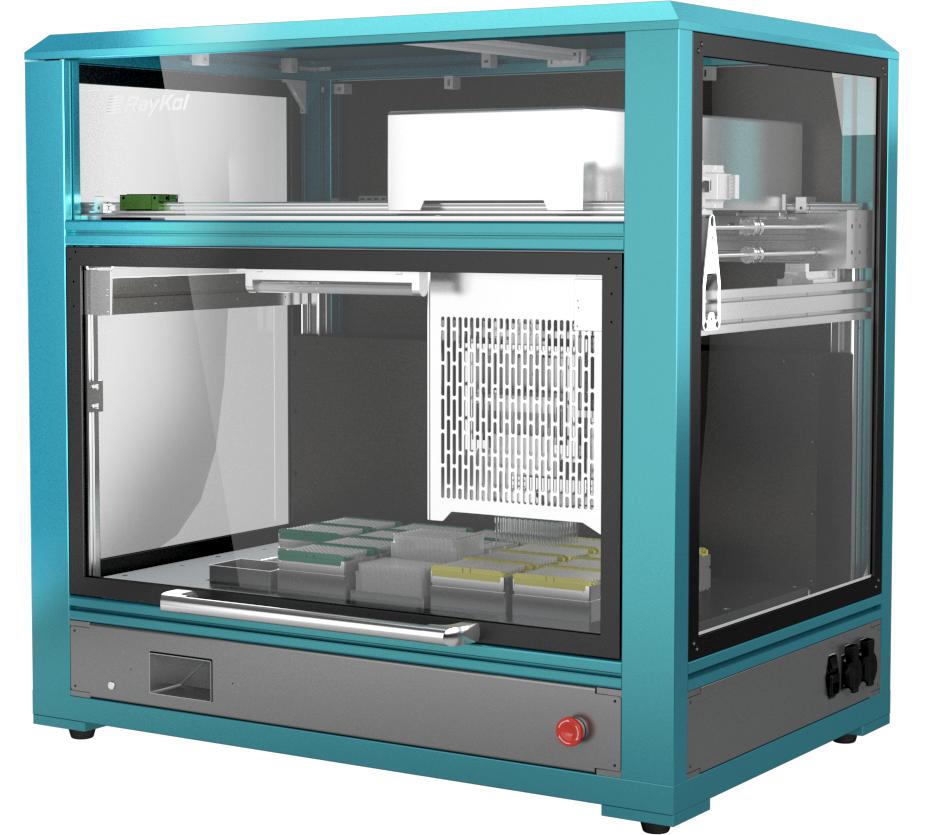

A high-throughput, high-recovery, high-safety-performance equipment with strong anti-interference capability and wide applicability, suitable for high-throughput processing of large cohort samples, achieving fully automated and standardized operations of mass spectrometry protein sample pretreatment.
Proteomics Sample Pretreatment Kit
(New Solid-Phase Alkylation Reagent)
The product is suitable for processing various sources of proteomics samples, such as cells, plasma, bacteria, tumor tissues, etc., using a new solid-phase alkylation reagent. Proteins can achieve rapid separation from other small molecules (such as sugars, salts, surfactants, lipids, etc.), improving protein purity and significantly reducing sample complexity. At the same time, the reagent surface has good hydrophilicity, significantly improving the recovery rate of proteins or enzymolysis products.

High Throughput
96-channel pipetting head, can handle up to 96 samples at one time, efficiently completing steps like waste aspiration in experimental processes;
Also features 8-channel pipetting functionality, enabling precise reagent dispensing;
Full process can complete pretreatment of 96 protein samples in 4-5 hours (specific time depending on the specific experimental process);
High Degree of Automation
Integrates a gripper for transferring standard SBS plates;
Integrates functional modules required for protein pretreatment such as reagent refrigeration, magnetic adsorption, and heating oscillation;
Standardized operations reduce errors in experimental processes, improving accuracy and stability;
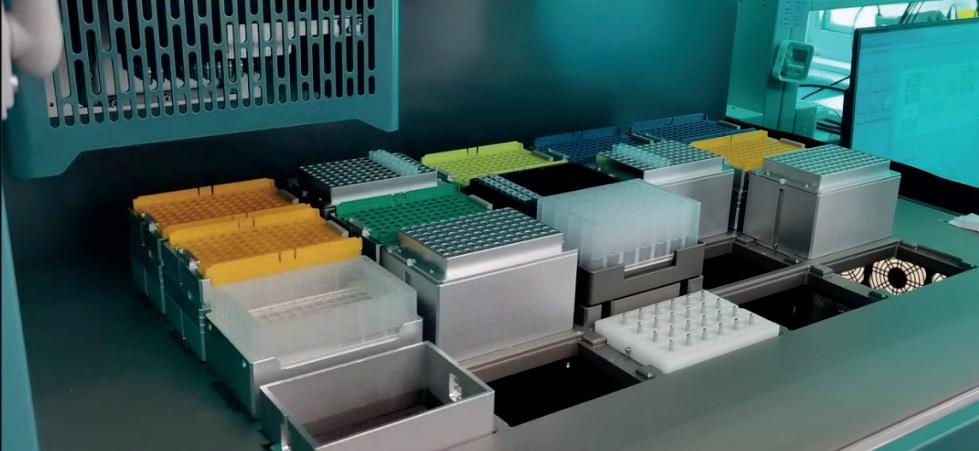

Strong Flexibility
The panel includes 18 SBS standard positions. Apart from functional modules, there are 15 positions for placing reagents and consumables;
Open platform with a variety of adapters, compatible with various reagent consumables from different brands;
User-friendly software interface, drag-and-drop layout, simple operation, parameter settings can be done independently for each step, experiment process can be stored, button start operation;
Safety
Configurable light shielding cover, with UV sterilization lamp;
Optionally equipped with positive and negative pressure HEPA filtration systems as needed, effectively preventing cross-contamination;
Material: 293T Cells
Experimental Method: Manual Operation3 Groups, Instrument Operation3 Groups
Q Exactive Mass Spectrometry Results as follows:
Table 1: Comparison of Protein Numbers and Zero-Missed-Cleavage Rate between Manual and Instrument Operations
Sample 293T Protein | Manual Handling | Instrument Handling | ||
Protein Number | Zero-Missed Cleavage Rate (%) | Protein Number | Zero-Missed Cleavage Rate (%) | |
Parallel Sample 1 | 3282 | 76.90 | 3168 | 75.02 |
| Parallel Sample 2 | 3164 | 75.52 | 3083 | 76.39 |
| Parallel Sample 3 | 3164 | 78.07 | 3064 | 76.95 |
| Average Value | 3203 | 76.03 | 3105 | 76.12 |
| STDEV | 68 | 1028 | 55 | 0.99 |
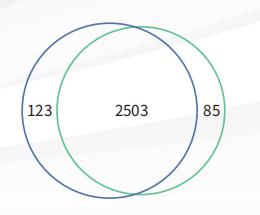
Figure 1 Venn diagram (blue: manual; green: instrument)
Experimental summary
The number of proteins that can be detected and the zero missed cutting rate after pretreatment of protein samples by manual operation and instrument operation are basically the same, meeting the expected requirements;
The Pierce correlation coefficient of protein types between manual operation and instrument operation is greater than 0.97, which is consistent with expectations;
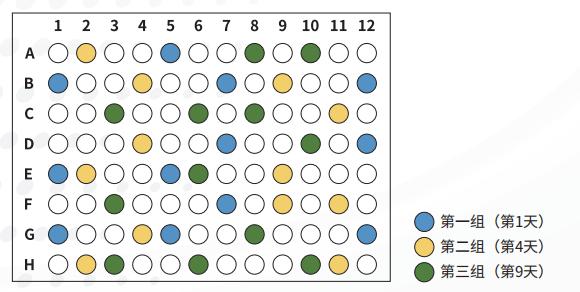
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of 96-well plate assay
As shown in Figure 2, a total of 96 samples were processed and divided into three groups for experiments. 36 samples were randomly selected for Q Exactive mass spectrometry detection. The results are as follows:
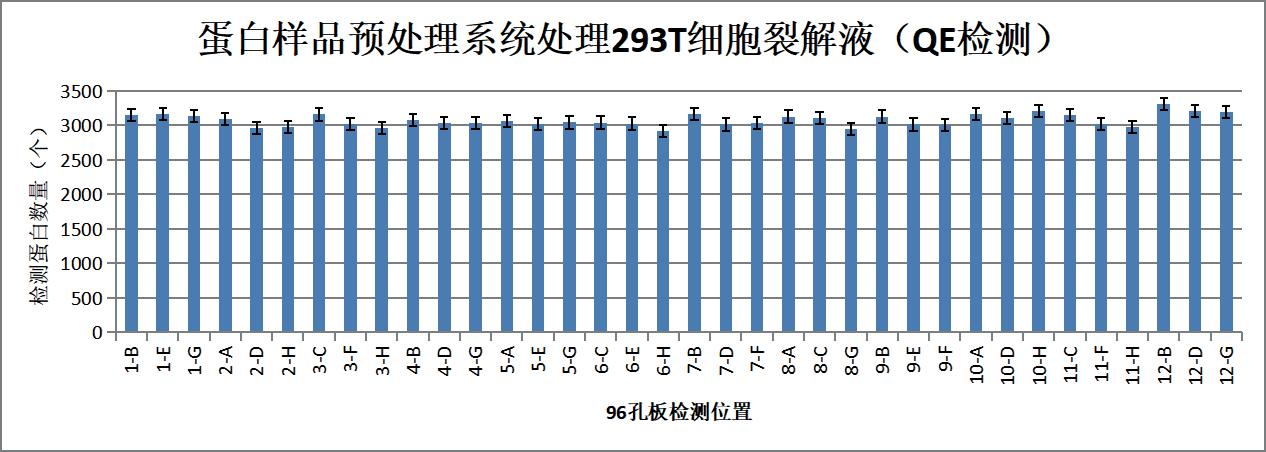
Figure 3 Number of proteins detected in 36 samples (units)
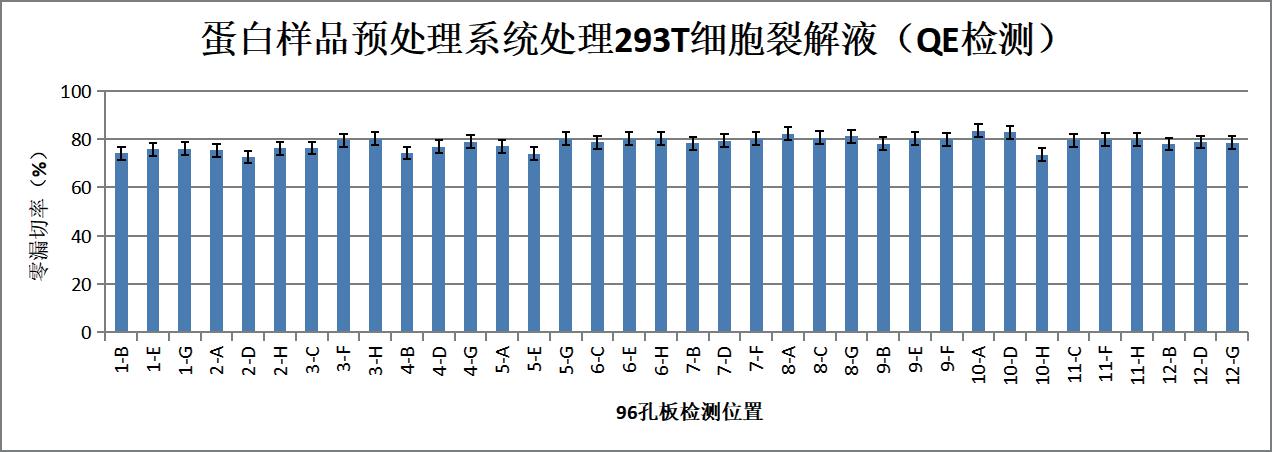
Figure 4 Zero missed cutting rate of 36 samples (%)
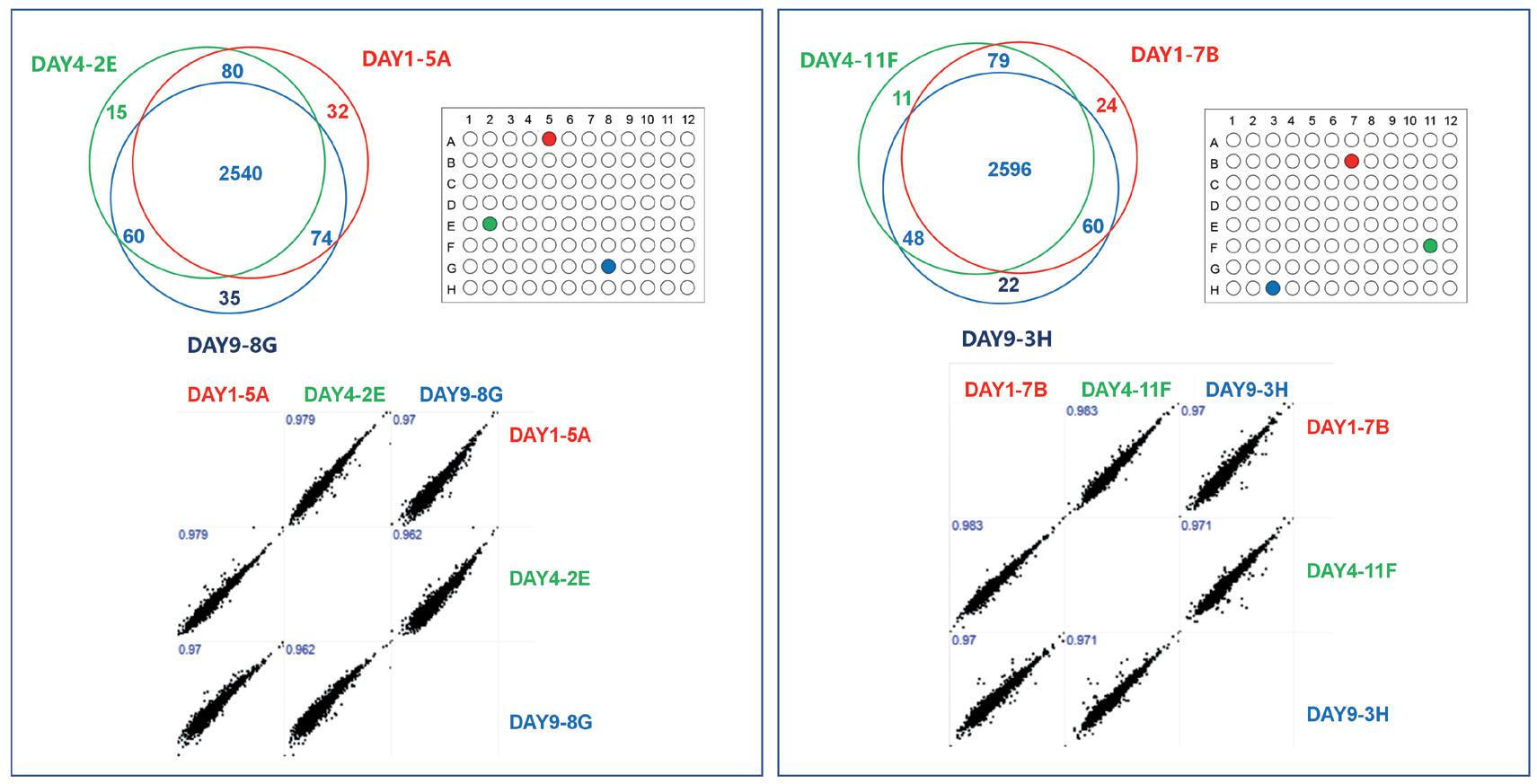
Figure 5 Random sample daytime comparison
Experimental summary
36 random samples detected 3074±89 proteins, zero missed cutting rate 78.32±2.66%, sample pretreatment results are normal and stable;
The Pierce correlation coefficient of 36 samples and the Pierce correlation coefficient of random samples during the day are between 0.955-0.989, meeting the index requirements and having good uniformity.
Clinical diagnosis, medication guidance, pathological mechanism research, discovery of disease markers, drug mechanism research.